
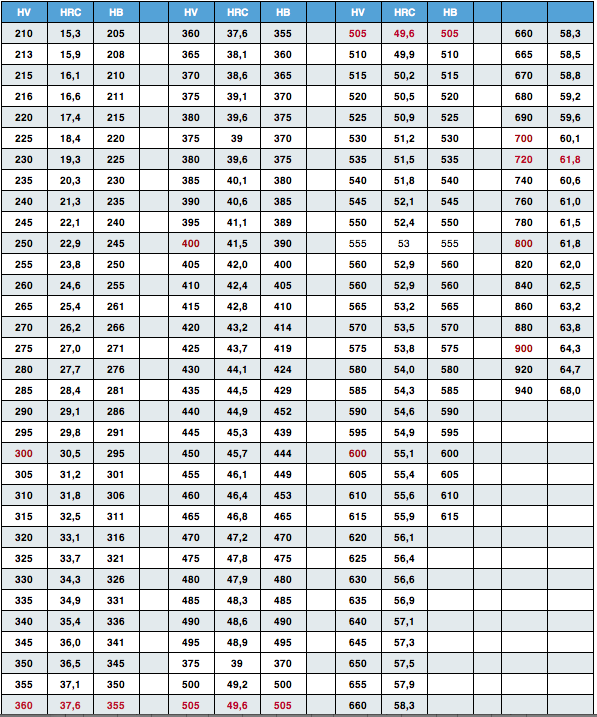
BS EN ISO 18265:2013'Metallic materials - Conversion of hardness values'.Some other hardness scales are included in the standards, but these are used less often.Ī useful conversion used extensively in applications involving H 2S is that 22 HRC (Rockwell C) is equivalent to 248 HV (Vickers), which is often rounded to 250 HV.Īn earlier standard, BS 860:1967, which has been superseded by BS EN ISO 18265:2003 gives the following equation for hardness conversion between Brinell and Vickers scales.Īs with all conversions, it must be appreciated that the conversion between hardness scales is approximate, not absolute. The conversions for these standards are not exactly the same, but are similar, incorporating Vickers, Brinell, Rockwell B, and Rockwell C hardness scales, and conversions for a limited number of material types. Two such standards are BS EN ISO 18265:2013, and ASTM E140: 2012.
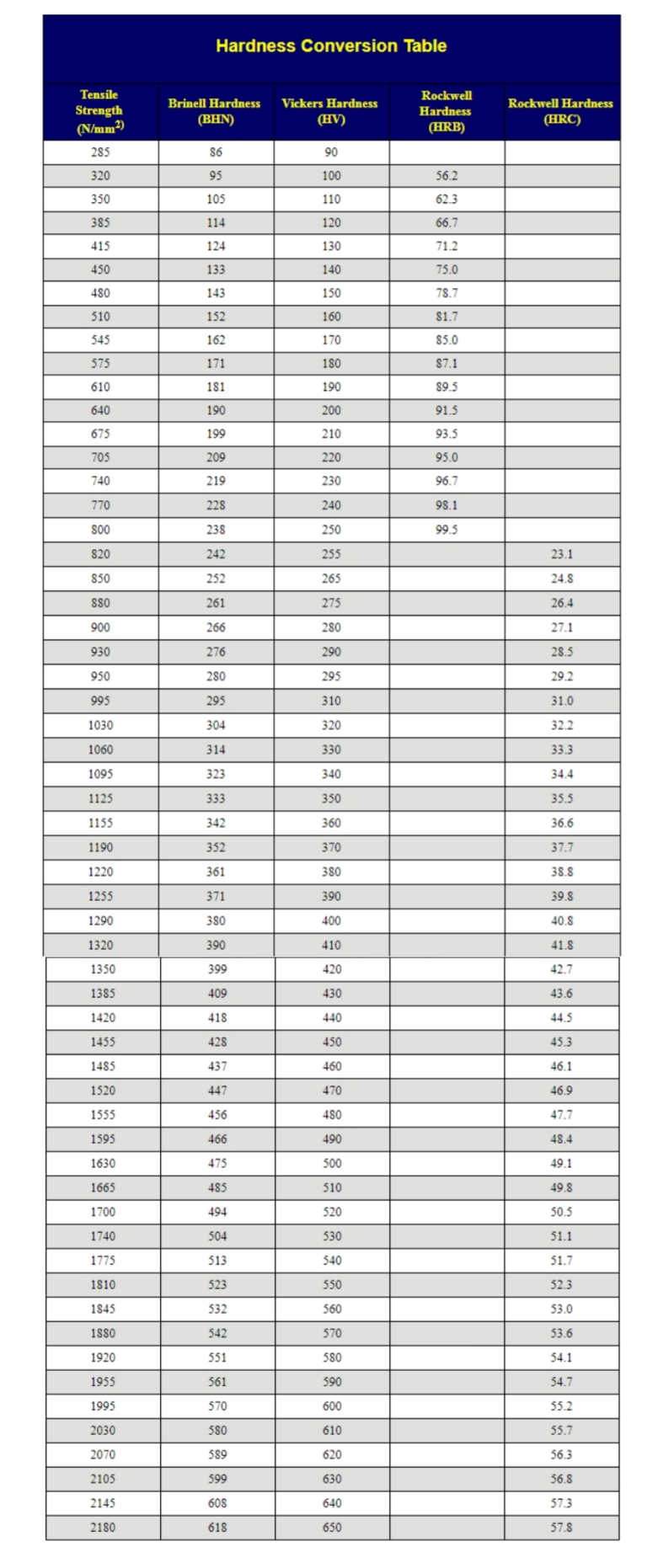
These have arisen from many hardness readings, the values have been plotted and a conversion established. However, a few national standards do list hardness conversion tables, and related equations. There is no direct, universally used correlation between the different hardness scales. National Structural Integrity Research Centre.Structural Integrity Research Foundation.** Above Brinell 451 HB tests were made with 10 mm carbide ball. * Below Brinell 101 tests were made with only 500 kg lodad and 10 mm ball. It is recommended that ASTM standards E 140, E 10, E18, E92, E110, E384 and A 370 ( involving hardness tests on metals) be reviewed prior to interpreting hardness conversion values. These values are consistent with ASTM E 140 Tables 1 and 2 and for non-austenitic steels. All relative hardness values on this card are averages of tests on various metals whose different properties prevent establishment of exact mathematical conversions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
